Welcome to statements of leadership, strategy, and decision-making as a process.
Statements Of Leadership
Leading is intentional
Path and goal need to be defined
Transformational leadership should be used to evolve executives
Leading is intentional. Intentional in a way that
- The environment is always uncertain and leaders need to be vigilant in understanding the uncertain environment in which they operate.
- Characteristics of executives need to be developed to align with uncertainty and strategic orientation. This relates closely with agile philosophies
- Passions of individuals should be brought alive in a way that correlates to the larger vision and mission of the organization.
Path and goal need to be defined
Leadership has been defined as the management of a firm’s capacity to set and achieve high-level goals for the organization. As such, the path and goals need to be defined for executives to achieve organizational goals that align with long-term strategic initiatives.
Leaders must identify blockages executives are experiencing between the path and the objective and apply different leadership styles to help executives/teams reach organizational goals. This can be executed by applying 4 different leadership styles in conjunction with a formula designed to remove blockages which are sx=y.
The leadership styles are.
Directive – Supportive – Participative – Achievement
The (sx = y) formula can be described as situation x being solved by leadership style Y.
Situation x – Blockage in path
Y – leadership style
Below are examples of different blockages that can be removed by the various leadership styles.
SX = Lack of knowledge of the subject needed to execute
Y = Supportive leadership style
SX = Executive can execute more complicated projects but needs to be challenged
Y = Achievement leadership style (mix of transactional and transformational techniques)
SX = Executive is completely stuck but can do it after being mentored
Y= Directive leadership style – Walk The Talk
SX = Project team is nearing the end of a project but is facing various challenges
Y= Participative Leadership Style – Input of ideas, knowledge, and creativity.
Ultimately, leaders need to pre-empt what blockages contributors might face based on their characteristics and plan leadership styles ahead of time to allow projects and processes to flow smoothly. To do this we can look at this from a project management perspective when planning a project and anticipating trade-offs. So while conducting a work breakdown structure, setting tasks and goals for managers and contributors, while conducting a risk assessment for the project, conduct smaller ones for individuals as well.
Often in project management, we spend a fair amount of time anticipating trade-offs, conducting risk assessments, perfecting work breakdown structures, and expecting the project to flow flawlessly. When problems arise in projects they could be due to the wrong leadership style being applied at the more critical stages of the project.
This leadership style can also be used to identify and assign tasks to contributors to challenge and evolve them so that they can better contribute to future projects that may be more advanced. Project and product project managers need to know and be taught the full context of the competitive environment along with the strategic direction of the firm. This way when executing projects, managers can challenge executives and evolve them in a way that aligns their skills with long-term strategic initiatives. Furthermore, this sets the foundation for innovation within project parameters to align with focused differentiated strategies.
Leadership is transformational.
The aim of transformational leadership is to connect followers with shared goals the firm needs to achieve. Transformational leadership influences followers as opposed to using power and reward to get things done. These can be best achieved through 2 leadership techniques: Intellectual Stimulation and Individualized Consideration.
Intellectual stimulation
Definition: Having a leader who encourages innovation and creativity, as well as critical thinking and problem-solving.
Example: Stimulate thoughts and ideas without criticism to allow executives to come up with new/innovative ways of getting things done.
Implementation: Offer reimagination of the project, insight into creativity, and solutions.
Individualized Consideration
Definition: Individualized Consideration is the extent to which a leader attends to each follower’s needs.
Example: Delegating challenging tasks to individuals who are deserving. This can be closely applied to an achievement-based leadership style.
Implementation: This is achieved by treating contributors according to their talents and knowledge. Identify and leverage the perception and needs of each individual to go beyond their self-interest to meet organizational goals.
Path-Goal and transformational leadership can be used in conjunction to continue evolving executives to take firms to new heights. Contributors need to be evolved in order for the firm to continue achieving high-level goals as the firm competes in an uncertain environment and stays relevant to market conditions. Every decision made by a leader should be done so with building processes that align with business strategy in mind. This leads us to the next section of this article, Statements of Strategy
Statements of Strategy
Strategy is a choice of how to place resources and sequence tactics
The point of strategy is to not go head to head with competitors and so capabilities should be developed and placed in a way that is unique
Strategy is executed through decision streams and so decision-making as a process should be implemented
Statements of strategy have been introduced in this article to fill the gaps between leading in a way that is intentional and decision-making as a process so that you completely understand that…
1. The point of leadership and decision-making is to execute strategy
2. Making decisions that consistently achieve an optimal outcome contributes to sustaining competitive strategy
3. To develop and align processes with the strategy (This helps with the creation of unique capabilities and in turn supports competitive strategy)
Strategy is a choice of how to place resources and sequence tactics
This is based on an analysis of what you think the present situation is and your prediction of what you think the truth is tomorrow.
You can only develop a competitive strategy once you thoroughly understand the competitive landscape, how competitors have placed resources, and how you predict they can develop and use these resources in the future.
This is why…
Tactics require observation and strategy requires deep thought upon tactics used in the landscape. (copyright Higher Media LTD)
This definition applies to all levels within strategic management ( corporate – business – functional – individual )
Functional example:
Marketing strategy – Allows for the implementation of limited resources on market opportunities to execute tactics that create and deliver value based on your analysis of the market.
The point of strategy is to not go head to head
Competitive Strategy is being unique in a way that exploits core competencies that is different from competitors to deliver a unique set of values to selected customer criteria.
Instead of being the best in the market, ask yourself how you can be the best company for your selected target market and build a profitable relationship with them. This will guide you away from what you think strategy is and what pursuing a true strategy really looks like.
Using Ikea as an example they aren’t the best company in the furniture market, but they are to their selected segments. Certain segments prefer more traditional forms of furniture vs Ikea’s vibrant build-your-own. What the build-and-play strategy does is allow for huge amounts of inventory. What this inventory system does is lay the foundation for economies of scale to be exploited. Think of the amount of furniture a traditional furniture store can stock by selling items that aren’t foldable vs the amount of inventory Ikea can hold simply due to the way the furniture is designed. This is the perfect example of a broad cost leadership strategy. Using strategic alliances with partners, Ikea outsourcing is primarily focused on dependency on capacity. Achieving economies of scale is essential to satisfying the selected segment competitively.
1 of Ikea’s competitive advantage’s intangible assets. More specifically, the effective partnership and management of dependence on capacity. A sustained advantage would be holding partners and internal business units to an innovation standard that supports IKEA’s pursuit of economies of scale and product choice. These standards could include the focus of resources on
- Research and development of the mechanisms of build and play
- Innovation in scale manufacturing.
Exploiting the capabilities of suppliers should be a high-level organizational goal.
These strategic attributes support the firm’s mission to be the best company for their customer.
If the build-and-play aspect of Ikea’s furniture enables inventory, dependence on capacity, and cost leadership. Innovation in this area should be a key focus.
Strategic focus
- Massive inventory
- Lower shipping costs
- Variety of products
- Strategic location
- Cost friendly
- Strategic partners
Strategy is executed through decision streams
Decision-making can be seen as one of the most important aspects of leadership as ultimately, it’s what enables and executes strategy.
Whether or not the strategy of the firm can be executed, comes down to a pattern of decisions that emerge from the day-to-day activities of actioning the tactics chosen to try and achieve the long-term goals. These tactics are executed best when rational thinking is applied by leaders. This leads us to ‘ Statements Of Decision Making ‘.
Statements of Decision Making
As we move forward into a world where strategy is driven by data, it’s smart to enhance the decision-making process within organizations by introducing frameworks, automation, and AI too;
- Make unbiased decisions
- Pursue strategy more rapidly
- Make decisions more efficiently and effectively
- Achieve optimal outcomes in a majority of situations
- Counter group think bias and ethical fading
Introducing decision-making as a process within large organizations is not a promise to make better decisions. It may though, provide a basis for general decisions to be more effective as well as enable the firm to make these decisions quickly and direct them more towards the strategic direction of the firm.
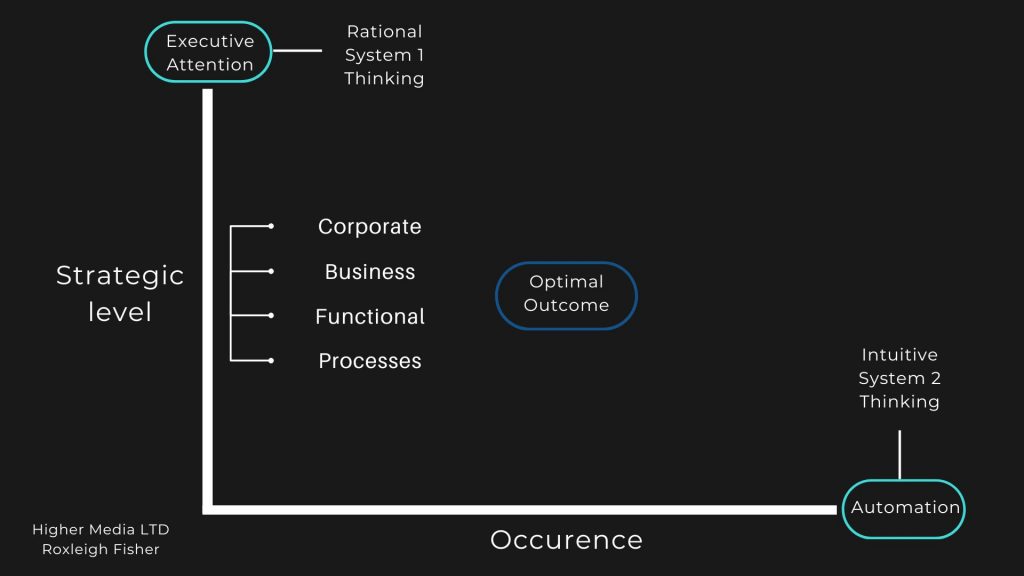
By categorizing decisions into a hierarchy, were able to define what kind of decisions need executive attention as well as what decisions can be automated. Without this, major decisions may not be given the attention they deserve in order for the optimal outcome to be achieved. Here we present a method/framework to achieve this.
The Framework ( ICDD by Higher Media LTD ) ( Framework available on request )
Identify – Categorize – Decide – Design
Identify & Categorize
Identify the different kinds of decisions that are made in the firm and how often they occur.
- What decisions involve challenging and developing executives?
- What are the bigger more critical decisions of the firm?
- How often are decisions made?
- What decisions or decision groups can be automated? These are generally the decisions that occur most often.
- How well are these decisions made?
Categorize decisions on how often they occur, what level of strategy ( Individual, functional, business, corporate ) they occur on, and how well these decisions are made.
Decide & Design
Decide which decisions could be made better and develop a process for these decisions to achieve optimal outcomes that contribute to strategic direction.
Design
Design and implement a process for how decisions are identified and how the outcomes of these decisions are judged and improved.
This framework and approach to how decisions are made can also be applied as an after-action review process for general project management.
Overview
Decision-making as a process and the various leadership techniques highlighted allow for smoother execution of high-level goals of the organization with the aim of achieving optimal outcomes. Understanding the effect of pre-empting blockages executives might face in conjunction with systematic and rational decision-making as a process can contribute to firms ultimately becoming more progressive in the way that they evolve to stay relevant and execute strategies.
Innovation within project parameters – This is when innovation occurs due to teams and executives being challenged while executing advanced projects. (higher media ltd)
Roxleigh Fisher
References
http://www.free-management-ebooks.com/faqld/leadership-05.htm
https://hbr.org/2009/11/make-better-decisions-2
Transformational Leadership: Towards Effective Governance in Nigeria – Adebayo A. Adanri, PhD
The University of Illinois IMBA (Managing The Organization) https://www.coursera.org/learn/managing-organization?specialization=strategic-leadership


